The calculation of the bending radius of the cable mainly depends on the diameter and material of the cable. The following are some common calculation methods and standards:
The allowable bending radius of a cable is usually several times its outer diameter. For example, if the outer diameter of the cable is 10 mm and the allowable bending radius is 15 times the outer diameter, the bending radius is:
15 × 10 = 150 mm
This means that the cable should form an arc when it is bent (turned), and the radius should be greater than or equal to 150mm.
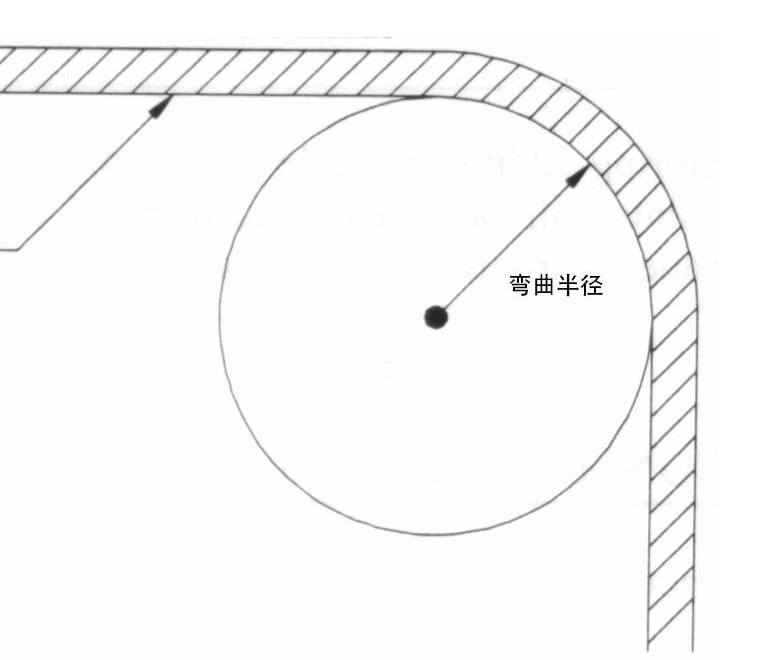
Different cable materials and structures require different bending radii. For example:
In addition, the calculation of bending radius for different types of cables, such as PVC cable, PE cable, XLPE cable, etc. may also be different.
The specific calculation of the cable bending radius should also refer to relevant industry standards and specifications. For example:
It is very important to correctly calculate and adhere to the bending radius of the cables:
In actual applications, the appropriate bending radius should be selected according to the specific cable type, diameter and use environment, and installation and operation should be carried out strictly in accordance with standards and specifications.